
Complete Guide to Gas Mixers and its various applications
Reference Guide for Plasma Cutting Gas Selection
The correct selection of gases for plasma cutting must take into account a number of factors. Some plasma cutting machines also allow you to select a specific gas for the plasma and a second gas for the protective atmosphere.
Table of contents:
1. How does the Plasma Cutting machine work?
The plasma cutting process works with a pressurized gas flow (1), heated electrically, being drained by the torch (2) in high flow through a small orifice (3 – nozzle). The resulting flux (4 – plasma) can melt and blow on most metals quite easily.
Plasma cutting torches generally use a copper nozzle to restrict the flow of gas with the arc flowing through it. This arc jumps from an electrode (5) on the torch to the conductive material being cut. This means that plasma cutting is used only for conductive materials, mainly carbon steel, stainless steel and aluminum.
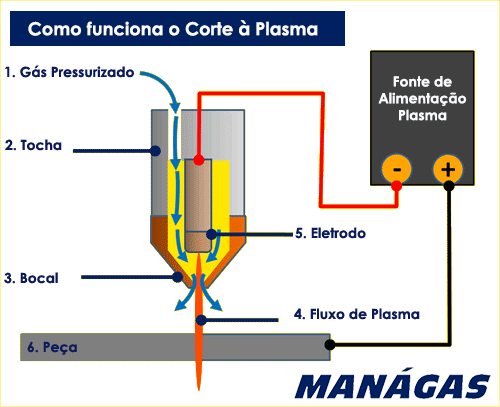
2. What is the most suitable gas for Plasma Cutting?
There are five main types of plasma gases used in CNC plasma cutting systems: compressed air, N2 (nitrogen), O2 (oxygen), H35 (argon-hydrogen) and F5 (hydrogen-nitrogen).
The choice of plasma gas suitable for your operation depends on several factors, including the material being cut, the quality of the cut, the thickness of the material, the consumable life and the cost of production.
Compressed Air
Compressed air is the most commonly used gas and the most versatile for lower current plasma cutting and works well for most metals up to 1 inch thick. Compressed air can also be used for gouging plasma on carbon steel.
However, a concern with air plasma is the weldability of the cutting edge. Some nitriding and oxidation of the cutting surface occurs with air plasma; this can cause porosity in the welds. Due to its versatility, good speed and low slag levels, compressed air can be a good option for many companies.

Nitrogen (N2)
Nitrogen is often used for higher current plasma systems and for cutting materials up to 3 inches thick, although for something more than an inch thick consider using argon-hydrogen. It is the best choice if you cut a lot of aluminum and stainless steel and the quality of the cut and the service life of the parts are excellent (more than 1000 starts are normal). Produces excellent quality cuts on most materials.

Oxygen (O2)
Oxygen is used when the highest quality mechanized cuts are desired from 1 to 1/4 inch thick carbon steel. The cut face is smooth and the slag is easy to remove.
Oxygen can also be used on stainless steel and aluminum, but it produces a rougher cut face. Plasma oxygen gas reacts with carbon steel to produce a finer spray of molten metal, each drop having a lower surface tension. This molten spray is more easily ejected from the cut.
The disadvantage of oxygen is the cost of gas and the useful life of consumable parts. However, state-of-the-art oxygen plasma systems use inert gases (such as nitrogen) with oxygen plasma to achieve a similar part life to nitrogen or air systems. These systems can have part life in the 800-1500-start range. The increased costs of consumables and gas are generally offset by a decrease in costly secondary operations to remove slag and straighten beveled parts.

H35 Gas Mixture (Argon-Hydrogen gas mixture)
Gas mixtures or gas mixers are generally used to cut stainless steel and aluminum (> 1/2 ″). The gas mixture normally used is 35% Hydrogen and 65% Argon (H-35).
They produce a clean, high-quality cutting face. Argon-Hydrogen is required for mechanized cutting of any material over 5 cm thick. This mixture also provides an excellent gas for plasma gouging in all materials.
Hydrogen with Argon is the hottest plasma gas and provides maximum cutting capacity. Some irregular slag may occur along the bottom edge. The disadvantage of this combination is its expense.

F5 Gas Mixture (Hydrogen-Nitrogen gas mixture)
The F5 gas mixture (5% Hydrogen and 95% Nitrogen) is mainly used for cutting stainless steel. The F5 blend provides fast, oxide-free cuts, however, Hydrogen gas introduces a lot of heat into the material. As a result, more slag formation, with the cut parts generally needing cleaning before proceeding to welding or painting operations. Using F5 gas mixtures can also be expensive. As an alternative, it is worth evaluating the investment in gas mixers.
3. Plasma Cutting gas selection reference table
Plasma Gas/Protection Gas
Air/Air
Carbon Steel
Economical, good cut quality and speed
Stainless Steel
Economical, good cut quality and speed
Aluminum
Economical, good cut quality and speed
Plasma Gas/Protection Gas
Oxygen/Air
Carbon Steel
Excellent quality/cutting speed, minimal slag
Stainless Steel
Not recommended
Aluminum
Not recommended
Plasma Gas/Protection Gas
Nitrogen/Carbon Dioxide CO2
Carbon Steel
Excellent part life, satisfactory cut quality, presence of slag
Stainless Steel
Excellent part life, good cut quality
Aluminum
Excellent part life, good cut quality
Plasma Gas/Protection Gas
Nitrogen/Air
Carbon Steel
Excellent part life, satisfactory cut quality, presence of slag
Stainless Steel
Excellent part life, good cut quality
Aluminum
Excellent part life, good cut quality
Plasma Gas/Protection Gas
Argon (Hydrogen/Nitrogen)
Carbon Steel
Not recommended
Stainless Steel
Excellent for thickness above ½”
Aluminum
Excellent for thickness above ½ ”
Plasma Gas/Protection Gas
F5 mix (Nitrogen/Hydrogen gas mix)
Carbon Steel
Not recommended
Stainless Steel
Good cut with excellent cutting speed for thicknesses below 0.375”
Aluminum
Excellent for thickness above ½”
4. Conclusion
Considering the cutting quality, productivity and economy of the plasma cutting process, the conclusion for choosing the ideal plasma gas and protective atmosphere is as follows:
• For mild steel, use oxygen plasma and air protection to obtain the best cut quality, the lowest slag levels, minimum rework, excellent weldability and the highest cutting speed/productivity.
• For the best cut quality on stainless steel and aluminum less than 1/2 inch, use nitrogen plasma and secondary air for a good balance between cut quality and cost. For a slightly better and faster cut, use CO2 as a secondary. If your system allows it, water protection will provide the best edge quality.
• For the best cut quality on stainless steel and thick aluminum, use argon-hydrogen with secondary nitrogen. CAUTION: Your system must be equipped for safe operation with argon-hydrogen gas.
• For a more economical cut, dry and clean compressor air is the best option for mild steel, stainless steel and aluminum.
QUESTIONS related to the Reference Guide for Gas Selection for Plasma Cutting?
Any questions regarding the reference guide for the selection of gases for Plasma Cutting, please contact us. Feel free to explore our product line of high performance gas mixers for Plasma Cutting.

Gas mixer designed and manufactured for the welding process, which allows mixing between 02 gases, with flow rate and outlet pressure control. From 0 to 100% content adjustable gas mixing output.

Compact gas mixer designed and manufactured for the welding process, which allows mixing between 02 gases, with outlet flow rate control. From 0 to 100% content adjustable gas mixing output. Requires cylinder/first stage pressure regulators for both input gases.
